Type 概述#
1
2
3
4
5
public interface Type {
default String getTypeName () {
return toString ();
}
}
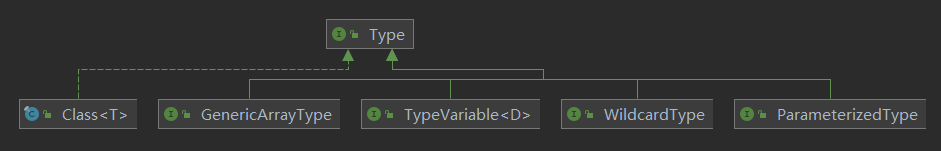
Type is the common super interface for all types in the Java programming language. These include raw types , parameterized types , array types , type variables and primitive types .
JDK 中的 Type 是一种高级抽象,其类图关系如下,它代表了 Java 中所有与 类型 相关的概念,此处的 类型 与我们常用的 基础数据类型 和 引用数据类型 的概念不同,它的抽象层级更高,概念更加宽泛,主要用于支持泛型中的类型处理。
除了我们熟悉的 Class 之外,还有如下子接口:
ParameterizedTypeTypeVariableGenericArrayTypeWildcardType
下面小节将分别使用示例代码进行介绍。
ParameterizedType#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public interface ParameterizedType extends Type {
Type [] getActualTypeArguments ();
Type getRawType ();
Type getOwnerType ();
}
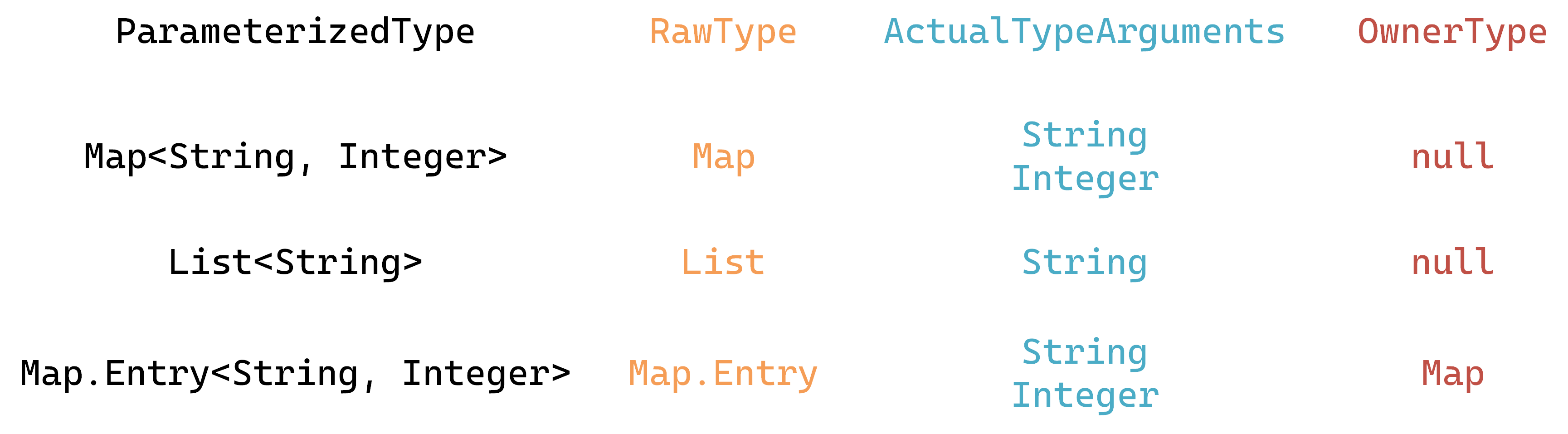
ParameterizedType 形如 List<String> ,即原生类型加上泛型参数的形式,其中,泛型参数可以有多个,并且既可以是实际具体类型(如 String),也可以是参数形式(如 T,K,E),还可以是通配符形式(如 ? extends Number)。各方法返回结果示例如下:
以下代码使用反射的方式进行实验,其中 getGenericType() 方法可以获取字段的泛型,对 getActualTypeArguments() 方法获取到的类型数组进行进一步的分析,可以发现它支持所有的 Type 子类型,代码有些部分暂时看不懂可以先放放,等后续章节看完再回头来看:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
public class ParameterizedTypeDemo < K extends Number > {
Map . Entry < K , String > entry ;
List < String > stringList ;
Map < K [] , ? extends Number > mapWithWildcard ;
Map < String , List < String >> mapWithList ;
OuterClass < K > . InnerClass < K > ownerTest ;
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
Class <?> clazz = ParameterizedTypeDemo . class ;
Field [] declaredFields = clazz . getDeclaredFields ();
printHorizonLine ();
Arrays . stream ( declaredFields ). forEach ( ParameterizedTypeDemo :: showFieldType );
}
private static void printHorizonLine () {
System . out . println ( "---------------------------------" );
}
private static void showFieldType ( Field field ) {
Type type = field . getGenericType ();
if ( type instanceof ParameterizedType ) {
printFieldTypeInfo ( field , type );
printHorizonLine ();
}
}
private static void printFieldTypeInfo ( Field field , Type type ) {
ParameterizedType parameterizedType = ( ParameterizedType ) type ;
Type rawType = parameterizedType . getRawType ();
Type [] actualTypeArguments = parameterizedType . getActualTypeArguments ();
Type ownerType = parameterizedType . getOwnerType ();
System . out . printf ( "Field '%s' ParameterizedType %s attrs: \n" , field . getName (), type . getTypeName ());
System . out . printf ( "[RawType]: %s, [OwnerType]: %s \n" ,
rawType , ownerType );
System . out . println ( "[ActualTypeArguments]:" );
Arrays . stream ( actualTypeArguments ). forEach ( ParameterizedTypeDemo :: printActualArguments );
}
private static void printActualArguments ( Type t ) {
if ( t instanceof ParameterizedType ) {
System . out . printf ( "(P) %s \n" , t );
} else if ( t instanceof TypeVariable ) {
System . out . printf ( "(T) %s \n" , t );
} else if ( t instanceof WildcardType ) {
System . out . printf ( "(W) %s \n" , t );
} else if ( t instanceof GenericArrayType ) {
System . out . printf ( "(A) %s \n" , t );
} else if ( t instanceof Class ) {
System . out . printf ( "(C) %s \n" , t );
}
}
}
class OuterClass < T > {
class InnerClass < S > {
}
}
输出结果为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
---------------------------------
Field ' entry ' ParameterizedType java . util . Map$Entry < K , java . lang . String > attrs :
[ RawType ] : interface java . util . Map$Entry , [ OwnerType ] : interface java . util . Map
[ ActualTypeArguments ] :
( T ) K
( C ) class java . lang . String
---------------------------------
Field ' stringList ' ParameterizedType java . util . List < java . lang . String > attrs :
[ RawType ] : interface java . util . List , [ OwnerType ] : null
[ ActualTypeArguments ] :
( C ) class java . lang . String
---------------------------------
Field ' mapWithWildcard ' ParameterizedType java . util . Map < K [] , ? extends java . lang . Number > attrs :
[ RawType ] : interface java . util . Map , [ OwnerType ] : null
[ ActualTypeArguments ] :
( A ) K []
( W ) ? extends java . lang . Number
---------------------------------
Field ' mapWithList ' ParameterizedType java . util . Map < java . lang . String , java . util . List < java . lang . String >> attrs :
[ RawType ] : interface java . util . Map , [ OwnerType ] : null
[ ActualTypeArguments ] :
( C ) class java . lang . String
( P ) java . util . List < java . lang . String >
---------------------------------
Field ' ownerTest ' ParameterizedType cn . liyangjie . spring . OuterClass < K > $InnerClass < K > attrs :
[ RawType ] : class cn . liyangjie . spring . OuterClass$InnerClass , [ OwnerType ] : cn . liyangjie . spring . OuterClass < K >
[ ActualTypeArguments ] :
( T ) K
---------------------------------
TypeVariable#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public interface TypeVariable < D extends GenericDeclaration > extends Type , AnnotatedElement {
Type [] getBounds ();
D getGenericDeclaration ();
String getName ();
AnnotatedType [] getAnnotatedBounds ();
}
TypeVariable 表示的是 类型参数 的概念,即泛型定义中使用到的 T, K, E 等,如 JDK 中提供的 List 类,其含有一个 TypeVariable 为 E。
1
public interface List < E > extends Collection < E > ...
再次观察 TypeVariable 接口可以发现其自身含有一个上界为 GenericDeclaration 的类型参数,其类图如下:
字面意义上,它表示的是 泛型声明 ,Java 规范中,泛型的定义可以出现在 类 和 方法 上(构造器也可归属于方法),正好对应了该上图中的 3 个实现类。因此 getGenericDeclaration() 方法是为了获取该参数所定义的「位置」。以下代码分别定义了 4 个 TypeVariable ,分别展示了 3 种不同位置及 Java8 后引入的 TypeAnnotation。
1
2
3
4
@Target ({ ElementType . TYPE_USE })
@Retention ( RetentionPolicy . RUNTIME )
public @interface TypeBoundAnnotationT {
}
1
2
3
4
@Target ({ ElementType . TYPE_USE })
@Retention ( RetentionPolicy . RUNTIME )
public @interface TypeBoundAnnotationE {
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
public class TypeVariableDemo < T extends @TypeBoundAnnotationT Comparable < T > ,
E extends @TypeBoundAnnotationT @TypeBoundAnnotationE Number &
@TypeBoundAnnotationE CharSequence > {
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
Class <?> typeVariableClazz = TypeVariableDemo . class ;
TypeVariable <? extends GenericDeclaration >[] typeParameters = typeVariableClazz . getTypeParameters ();
printHorizonLine ();
Arrays . stream ( typeParameters ). forEach ( TypeVariableDemo :: showTypeVariable );
Class <?> methodAndConstructorTestClazz = MethodAndConstructorTest . class ;
Constructor <?>[] declaredConstructors = methodAndConstructorTestClazz . getDeclaredConstructors ();
Method [] declaredMethods = methodAndConstructorTestClazz . getDeclaredMethods ();
showMethodTypeVariables ( declaredConstructors );
showMethodTypeVariables ( declaredMethods );
}
private static void printHorizonLine () {
System . out . println ( "---------------------------------" );
}
private static void showTypeVariable ( TypeVariable <? extends GenericDeclaration > tv ) {
String name = tv . getName ();
Type [] bounds = tv . getBounds ();
AnnotatedType [] annotatedBounds = tv . getAnnotatedBounds ();
GenericDeclaration genericDeclaration = tv . getGenericDeclaration ();
System . out . printf ( "[TypeVariableName]: %s\n" , name );
System . out . printf ( "[Bounds]: %s\n" , Arrays . toString ( bounds ));
System . out . printf ( "[GenericDeclaration]: %s\n" , genericDeclaration );
System . out . println ( "[AnnotatedBounds]: " );
Arrays . stream ( annotatedBounds ). forEach ( a -> {
System . out . printf ( "%s\n" , Arrays . toString ( a . getAnnotations ()));
});
printHorizonLine ();
}
private static void showMethodTypeVariables ( GenericDeclaration [] declaredConstructors ) {
Arrays . stream ( declaredConstructors ). forEach ( c -> {
TypeVariable <?>[] constructorTypeParameters = c . getTypeParameters ();
Arrays . stream ( constructorTypeParameters ). forEach ( TypeVariableDemo :: showTypeVariable );
});
}
}
class MethodAndConstructorTest {
< K > MethodAndConstructorTest ( K k ){}
public < S > void methodTest ( S s ){}
}
输出结果如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
---------------------------------
[ TypeVariableName ] : T
[ Bounds ] : [ java . lang . Comparable < T >]
[ GenericDeclaration ] : class cn . liyangjie . spring . TypeVariableDemo
[ AnnotatedBounds ] :
[ @cn.liyangjie.spring.TypeBoundAnnotationT () ]
---------------------------------
[ TypeVariableName ] : E
[ Bounds ] : [ class java . lang . Number , interface java . lang . CharSequence ]
[ GenericDeclaration ] : class cn . liyangjie . spring . TypeVariableDemo
[ AnnotatedBounds ] :
[ @cn.liyangjie.spring.TypeBoundAnnotationT (), @cn.liyangjie.spring.TypeBoundAnnotationE () ]
[ @cn.liyangjie.spring.TypeBoundAnnotationE () ]
---------------------------------
[ TypeVariableName ] : K
[ Bounds ] : [ class java . lang . Object ]
[ GenericDeclaration ] : cn . liyangjie . spring . MethodAndConstructorTest ( java . lang . Object )
[ AnnotatedBounds ] :
[]
---------------------------------
[ TypeVariableName ] : S
[ Bounds ] : [ class java . lang . Object ]
[ GenericDeclaration ] : public void cn . liyangjie . spring . MethodAndConstructorTest . methodTest ( java . lang . Object )
[ AnnotatedBounds ] :
[]
---------------------------------
GenericArrayType#
1
2
3
public interface GenericArrayType extends Type {
Type getGenericComponentType ();
}
GenericArrayType 表示形如 T[], T[][] 等 泛型数组 ,它有一个方法,获取数组中所存储元素的 Type。示例代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public class GenericArrayTypeDemo < T > {
T [] tA ;
T [][] tAA ;
List < T >[] listA ;
List <? extends T >[] wildcardListA ;
String [] stringA ;
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
Class <?> clazz = GenericArrayTypeDemo . class ;
Field [] fields = clazz . getDeclaredFields ();
Arrays . stream ( fields ). forEach ( GenericArrayTypeDemo :: showGenericTypeComponentType );
}
private static void showGenericTypeComponentType ( Field f ) {
String fieldName = f . getName ();
Type fieldType = f . getGenericType ();
if ( fieldType instanceof GenericArrayType ) {
GenericArrayType genericArrayType = ( GenericArrayType ) fieldType ;
System . out . printf ( "[Field: %s] Component Type is: %s\n" , fieldName , genericArrayType . getGenericComponentType ());
} else {
System . out . printf ( "[Field: %s] is not GenericArrayType\n" , fieldName );
}
}
}
输出结果如下:
1
2
3
4
5
[ Field : tA ] Component Type is : T
[ Field : tAA ] Component Type is : T []
[ Field : listA ] Component Type is : java . util . List < T >
[ Field : wildcardListA ] Component Type is : java . util . List <? extends T >
[ Field : stringA ] is not GenericArrayType
GenericType 相对来说还是好理解的,数组中的元素类型即为数组拿掉一个 [] 符号后对应的类型。
为了提升理解,这里留下一个问题:上述输出结果中, T, T[], List<T>, List<? extends T> 分别是什么类型?
1
2
3
4
[ Field: tA's component type] is TypeVariable
[Field: tAA' s component type] is GenericArrayType
[ Field: listA's component type] is ParameterizedType
[Field: wildcardListA' s component type] is ParameterizedType
WildcardType#
1
2
3
4
5
6
public interface WildcardType extends Type {
Type [] getUpperBounds ();
Type [] getLowerBounds ();
}
顾名思义,它表示的是 ? extends Number 形式的 通配符类型 ,接口中的两个方法也比较好理解,分别代表通配符的上界和下界。示例代码如下,为了简单起见,仅仅定义了一个 Field,且使用的时候直接取数组下标 0:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class WildcardTypeDemo {
List <? extends Number > wildcardList ;
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
Class <?> clazz = WildcardTypeDemo . class ;
Field wildcardField = clazz . getDeclaredFields () [ 0 ] ;
Type genericType = wildcardField . getGenericType (); //List<? extends Number>
if ( genericType instanceof ParameterizedType ) {
ParameterizedType parameterizedType = ( ParameterizedType ) genericType ;
Type actualTypeArgument = parameterizedType . getActualTypeArguments () [ 0 ] ; // ? extends Number
if ( actualTypeArgument instanceof WildcardType ) {
WildcardType wildcardType = ( WildcardType ) actualTypeArgument ;
System . out . printf ( "[Field %s is WildcardType]: %s, its upper bound is %s and lower bound is %s" ,
wildcardField . getName (), wildcardType ,
Arrays . toString ( wildcardType . getUpperBounds ()),
Arrays . toString ( wildcardType . getLowerBounds ()));
}
}
}
}
输出结果为:
1
[ Field wildcardList is WildcardType ] : ? extends java . lang . Number , its upper bound is [ class java . lang . Number ] and lower bound is []
Spring 中的 ResolvableType#
惯例先贴出 Spring 官方对于该类的简介:
Encapsulates a Java Type, providing access to supertypes, interfaces, and generic parameters along with the ability to ultimately resolve to a Class.
ResolvableType s may be obtained from fields, method parameters, method returns or classes. Most methods on this class will themselves return ResolvableType s, allowing easy navigation.
该类封装了 Java 原生的 Type 类型,提供了获取父类、接口、泛型参数的服务,同时能够最终将结果解析为 Class 类型。
ResolvableTypes 可以使用 字段 、方法参数、方法返回值、Class 等方式获取。该类中的大部分方法都将返回ResolvableTypes,方便后续的调用。
官方提供的示例代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
private HashMap < Integer , List < String >> myMap ;
public void example () {
ResolvableType t = ResolvableType . forField ( getClass (). getDeclaredField ( "myMap" ));
t . getSuperType (); // AbstractMap<Integer, List<String>>
t . asMap (); // Map<Integer, List<String>>
t . getGeneric ( 0 ). resolve (); // Integer
t . getGeneric ( 1 ). resolve (); // List
t . getGeneric ( 1 ); // List<String>
t . resolveGeneric ( 1 , 0 ); // String
}
ResolvableType 在 Spring 事件机制中的应用#
Spring 的事件机制(观察者模式)使用到了 ResolvableType 对广播的事件进行筛选,使得某监听器仅能监听某类型的事件,示例如下:自定义事件 MyEvent 及监听器 MyListener,该监听器指定泛型为 MyEvent:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class MyListener implements ApplicationListener < MyEvent > {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent ( MyEvent event ) {
System . out . printf ( "My Event, current person: %s %n" , event . getSource ());
}
}
class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L ;
public MyEvent ( Object source ) {
super ( source );
}
}
同时,再定义一个监听器,指定其泛型为 ContextRefreshedEvent,在Spring的 finishRefresh 阶段会由容器发布该事件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class ContextRefreshedListener implements ApplicationListener < ContextRefreshedEvent > {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent ( ContextRefreshedEvent event ) {
System . out . printf ( "ContextRefreshed, current source: %s %n" , event . getSource ());
}
}
main 方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext ();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader ( context );
reader . loadBeanDefinitions ( "META-INF/overview.xml" );
// 此过程中会由context发布ContextRefreshedEvent
context . refresh ();
System . out . println ( "--------------------------------" );
// 发布自定义的MyEvent
context . publishEvent ( new MyEvent ( SpringIocDemo . class ));
}
结果如下:
1
2
3
ContextRefreshed , current source : org . springframework . context . support . GenericApplicationContext @6acbcfc0
--------------------------------
My Event , current person : class cn . liyangjie . spring . SpringIocDemo
可以发现,两个监听器监听的事件不同,不会互相影响,这正是使用了 ResolvableType 对泛型进行了处理,核心代码位于 AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster 如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
protected boolean supportsEvent (
ApplicationListener <?> listener , ResolvableType eventType , @Nullable Class <?> sourceType ) {
GenericApplicationListener smartListener = ( listener instanceof GenericApplicationListener ?
( GenericApplicationListener ) listener : new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter ( listener ));
return ( smartListener . supportsEventType ( eventType ) && smartListener . supportsSourceType ( sourceType ));
}
可以看到,将原始的 ApplicationListener 转换为了 GenericApplicationListenerAdapter,该适配器的构造器如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public GenericApplicationListenerAdapter ( ApplicationListener <?> delegate ) {
Assert . notNull ( delegate , "Delegate listener must not be null" );
this . delegate = ( ApplicationListener < ApplicationEvent > ) delegate ;
this . declaredEventType = resolveDeclaredEventType ( this . delegate );
}
@Nullable
private static ResolvableType resolveDeclaredEventType ( ApplicationListener < ApplicationEvent > listener ) {
ResolvableType declaredEventType = resolveDeclaredEventType ( listener . getClass ());
if ( declaredEventType == null || declaredEventType . isAssignableFrom ( ApplicationEvent . class )) {
Class <?> targetClass = AopUtils . getTargetClass ( listener );
if ( targetClass != listener . getClass ()) {
declaredEventType = resolveDeclaredEventType ( targetClass );
}
}
return declaredEventType ;
}
@Nullable
static ResolvableType resolveDeclaredEventType ( Class <?> listenerType ) {
ResolvableType eventType = eventTypeCache . get ( listenerType );
if ( eventType == null ) {
// 1位置,重点!!
eventType = ResolvableType . forClass ( listenerType ). as ( ApplicationListener . class ). getGeneric ();
eventTypeCache . put ( listenerType , eventType );
}
return ( eventType != ResolvableType . NONE ? eventType : null );
}
代码中的 1 位置为重点部分, ResolvableType 解析了 ApplicationListener 具体的泛型类型。最后, supportsEventType 方法调用了 ResolvableType 的 isAssignableFrom 方法,以便监听器能接收泛型声明的类型及其子类事件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public boolean supportsEventType ( ResolvableType eventType ) {
if ( this . delegate instanceof GenericApplicationListener ) {
return (( GenericApplicationListener ) this . delegate ). supportsEventType ( eventType );
}
else if ( this . delegate instanceof SmartApplicationListener ) {
Class <? extends ApplicationEvent > eventClass = ( Class <? extends ApplicationEvent > ) eventType . resolve ();
return ( eventClass != null && (( SmartApplicationListener ) this . delegate ). supportsEventType ( eventClass ));
}
else {
// 1位置,重点
return ( this . declaredEventType == null || this . declaredEventType . isAssignableFrom ( eventType ));
}
}
现新增一个事件 MyEventChild,继承 MyEvent,并在代码中发布该事件,可以发现 MyListener 也能接收到该事件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
class MyEventChild extends MyEvent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L ;
public MyEventChild ( Object source ) {
super ( source );
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext ();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader ( context );
reader . loadBeanDefinitions ( "META-INF/overview.xml" );
// 此过程中会由context发布ContextRefreshedEvent
context . refresh ();
System . out . println ( "--------------------------------" );
// 发布自定义的MyEvent
context . publishEvent ( new MyEvent ( SpringIocDemo . class ));
// 将事件源修改为特定字符串以区分
context . publishEvent ( new MyEventChild ( "My Event Child" ));
}
结果如下:
1
2
3
4
ContextRefreshed , current source : org . springframework . context . support . GenericApplicationContext @6acbcfc0
--------------------------------
My Event , current person : class cn . liyangjie . spring . SpringIocDemo
My Event , current person : My Event Child